What is VMware vSAN:-
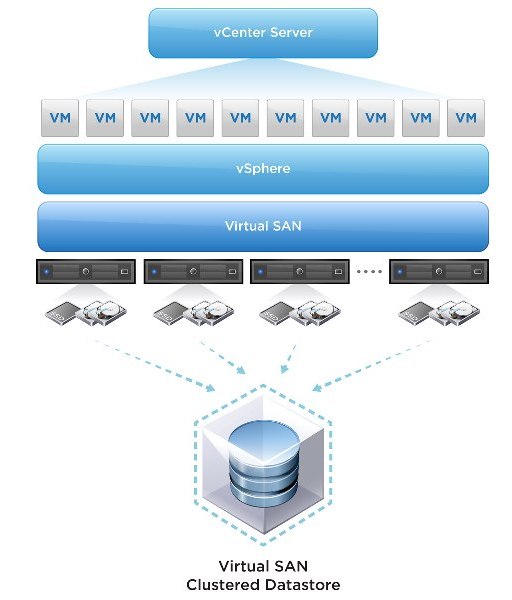
VMware Virtual SAN or we call it vSAN which was introduced back in 2013. In simple word if I would say, vSAN is a software based distributed storage solution that pools together direct-attached storage devices across a VMware vSphere cluster to create a distributed, shared data store. You can also refer to it as hyper-converged, or can consider it as software defined storage and some even referred to is as hypervisor converged at some point. VMware vSAN is fully integrated with VMware vSphere. There is very simple configuration which required for cnfiguring vSAN. If you know how to enable HA and DRS, then you know how to configure vSAN. Of course you will need to have a vSAN Network, and you achieve this by creating a VMkernel interface and enabling vSAN on it. vSAN works with L2 and L3 networks, and as of vSAN 6.6 no longer requires multicast to be enabled on the network. If I will go through with a quick overview of vSAN, here it is.
Overview of VSAN:-
- VSAN pools the locally attached storage from members of a VSAN–enabled cluster and presents the aggregated pool back to all hosts within the cluster.
- It has multiple disks presented to multiple hosts
- VSAN does not require any additional software installations.
- It is built directly into ESXi itself. Managed from vCenter Server.
- VSAN is compatible with all the other cluster features that vSphere offers, such as vMotion, HA, and DRS.
- We can even use Storage DRS to migrate VMs on or off a VSAN datastore.
- VSAN uses the disks directly attached to the ESXi hosts and is simple to set up.
- VSAN uses the concept calling RAIN, or reliable array of independent nodes.
- VSAN uses a combination of vSphere APIs for Storage Awareness (VASA) and storage policies to ensure that VMs are located on more than one disk and/or host to achieve their performance and availability requirements.
- VMware recommends 10 Gbps networking between ESXi hosts when using VSAN.
Requirements for VSAN:-
- ESXi 5.5 or newer hosts
- vCenter 5.5 or newer
- One or more SSDs per host
- One or more HDDs per host for hybrid mode
- Storage controllers must be on the VSAN HCL
- Minimum of three hosts per VSAN cluster
- Maximum of 64 hosts per VSAN cluster
- 1 Gbps network between hosts (10 Gbps highly recommended)
Types of VSAN Configuration
- Hybrid
- All SSD(Flash Only Disconnect)
Hybrid:
It uses both SSD and magnetic hard disks.
VSAN requires at least one flash-based device in
each host.
Hybrid VSANs use the SSD as a read and write cache just as some external SANs do.
W hen blocks are written to the underlying datastore, they are written to the SSDs first, and later the data can be relocated to the (spinning) HDDs.
VSAN’s read/write cache ratio is 70 percent read, 30 percent write.
All SSD:
It uses all SSD Disks.
There are many reason why customers are more intersted in choosing VSAN for their SDDC environment. Here are few of them:
- Integrated with vSphere which becomes more easier to manage and use existing tools
- Provides deduplication and data encryption
- Low Latency
- Lowering the CAPEX
- Enable fast delivery of services in less human efforts
- Save unsed storage from ESXi
- Easy to migrate to Cloud
- Low Risk
- High Controlling
- Simplify Day to Day Management
- Reduce TCO
- Automation
- Availability
- Security
- Reliability
- Scalability
- Management